Database Automation Series - Automated Indexes
Rate this podcast
Managing databases can be difficult, but it doesn't have to be. Most
aspects of database management can be automated, and with a platform
such as MongoDB Atlas, the tools are not only available, but they're
easy to use. In this series, we'll chat with Rez
Kahn, Lead Product Manager at
MongoDB, to learn about some of the ways Atlas automates the various
tasks associated with deploying, scaling, and ensuring efficient
performance of your databases. In this first part of the series, we'll
focus on a feature built into Atlas, called Index Autopilot.
Nic Raboy (00:56): Rez, thanks for taking the time to be on this
podcast episode. Before we get into the core material of actually
talking about database management and the things that you can automate,
let's take a step back, and why don't you tell us a little bit about
yourself?
Rez Kahn (01:10): Cool. Happy to be here, Nick. My name's Rez. I am a
lead product manager at MongoDB, I work out of the New York office. My
team is roughly responsible for making sure that the experience of our
customers are as amazing as possible after they deploy their first
application in MongoDB, which means we work on problems such as how we
monitor MongoDB. How we make sure our customers can diagnose issues and
fix issues that may come up with MongoDB, and a whole host of other
interesting areas, which we're going to dive into throughout the
podcast.
Nic Raboy (01:55): So, when you're talking about the customer success,
after they've gotten started on MongoDB, are you referencing just Atlas?
Are you referencing, say, Realm or some of the other tooling that
MongoDB offers as well? You want to shed some light?
Rez Kahn (02:10): Yeah, that's a really good question. Obviously, the
aspiration of the team is to help with all the products which MongoDB
supports today, and will eventually support in the future. But for the
time being, our focus has been on how do we crush the Atlas experience
and make it as magical of an experience as possible after a user
[inaudible 00:02:29] the first application.
Michael Lynn (02:30): How long have you been with MongoDB and what
were you doing prior to coming on board?
Rez Kahn (02:35): Well, I've been with MongoDB for a couple of years
now. Before joining MongoDB, I used to work in a completely different
industry advertising technology. I spent five years at a New York
startup called AppNexus, which eventually got sold to AT&T, and at
AppNexus, I was a product manager as well. But instead of building
databases, or helping manage databases better, I built products to help
our customers buy ads on the internet more effectively. A lot of it was
machine learning-based products. So, this would be systems to help
optimize how you spend your advertising dollars.
Rez Kahn (03:18): The root of the problem we're trying to solve is
figuring out which ads customers would click on and eventually purchase
a product based out of. How do we do that as effectively and as
efficiently as possible? Prior to AppNexus, I actually spent a number of
years in the research field trying to invent new types of materials to
build microchips. So, it was even more off-base compared to what I'm
doing today, but it's always very interesting to see the relationship
between research and product management. Eventually, I found it was
actually a very good background to have to be a good product manager.
Michael Lynn (03:59): Yeah, I would imagine you've got to be pretty
curious to work in that space, looking for new materials for chips.
That's pretty impressive. So, you've been on board with MongoDB for five
years. Did you go right into the Atlas space as a product manager?
Rez Kahn (04:20): So, I've been with MongoDB for two years, and yes-
Michael Lynn (04:22): Oh, two years, sorry.
Rez Kahn (04:23): No worries. I got hired as a, I think, as the second
product or third product manager for Atlas, and have been very lucky to
work with Atlas when it was fairly small to what is arguably a very
large part of MongoDB today.
Michael Lynn (04:42): Yeah. It's huge. I remember when I started,
Atlas didn't exist, and I remember when they made the first initial
announcements, internal only, about this product that was going to be in
the cloud. I just couldn't picture it. It's so funny to now see it, it's
become the biggest, I think arguably, the biggest part of our business.
I remember watching the chart as it took more and more of a percentage
of our gross revenue. Today, it's a phenomenal story and it's helping so
many people. One of the biggest challenges I had even before coming on
board at MongoDB was, how do you deploy this?

Michael Lynn (05:22): How do you configure it? If you want high
availability, it's got it. MongoDB has it built in, it's built right in,
but you've got to configure it and you've got to maintain it and you've
got to scale it, and all of those things can take hours, and obviously,
effort associated with that. So, to see something that's hit the stage
and people have just loved it, it's just been such a success. So,
that's, I guess, a bit of congratulations on Atlas and the success that
you've experienced. But I wonder if you might want to talk a little bit
about the problem space that Atlas lives in. Maybe touch a little bit
more on the elements of frustration that DBAs and developers face that
Atlas can have an impact on.
Rez Kahn (06:07): Yeah, totally. So, my experience with MongoDB is
actually very similar to yours, Mike. I think I first started, I first
used it at a hackathon back in 2012. I remember, while getting started
with it was very easy, it took us 10 minutes, I think, to run the first
query and get data from MongoDB. But once we had to deploy that app into
production and manage MongoDB, things became a little bit more tricky.
It takes us a number of hours to actually set things up, which is a lot
at the hackathon because you got only two hours to build the whole
thing. So, I did not think too much about the problem that I experienced
in my hackathon day, when I was doing the hackathon till I came to
MongoDB.
Rez Kahn (06:58): Then, I learned about Atlas and I saw my manager
deploy an Atlas cluster and show me an app, and the whole experience of
having an app running on a production version of MongoDB within 20
minutes was absolutely magical. Digging deeper into it, the problem we
were trying to solve is this, we know that the experience of using
MongoDB is great as a developer. It's very easy and fast to build
applications, but once you want to deploy an application, there is a
whole host of things you need to think about. You need to think about
how do I configure the MongoDB instance to have multiple nodes so that
if one of those nodes go down, you'll have a database available.
Rez Kahn (07:50): How do I configure a backup of my data so that
there's a copy of my data always available in case there's a
catastrophic data loss? How do I do things like monitor the performance
of MongoDB, and if there's a performance degradation, get alerted that
there's a performance degradation? Once I get alerted, what do I need to
do to make sure that I can fix the problem? If the way to fix the
problem is I need to have a bigger machine running MongoDB, how do I
upgrade a machine while making sure my database doesn't lose
connectivity or go down? So, those are all like not easy problems to
solve.
Rez Kahn (08:35): In large corporations, you have teams of DBS who do
that, in smaller startups, you don't have DBS. You have software
engineers who have to spend valuable time from their day to handle all
of these operational issues. If you really think about it, these
operational issues are not exactly value added things to be working on,
because you'd rather be spending the time building, differentiating
features in your application. So, the value which Atlas provided is we
handle all these operational issues for you. It's literally a couple of
clicks before you have a production into the MongoDB running, with
backup, monitoring, alerting, all those magically set up for you.
Rez Kahn (09:20): If you need to upgrade MongoDB instances, or need to
go to a higher, more powerful instance, all those things are just one
click as well, and it takes only a few minutes for it to be configured
for you. So, in other words, we're really putting a lot of time back
into the hands of our customers so that they can focus on building,
writing code, which differentiates their business as opposed to spending
time doing ops work.
Michael Lynn (09:45): Amazing. I mean, truly magical. So, you talked
quite a bit about the space there. You mentioned high availability, you
mentioned monitoring, you mentioned initial deployment, you mentioned
scalability. I know we talked before we kicked the podcast off, I'd love
for this to be the introduction to database management automation.
Because there's just so much, we could probably make four or five
episodes alone, but, Nick, did you have a question?
Nic Raboy (10:20): Yeah, I was just going to ask, so of all the things
that Atlas does for us, I was just going to ask, is there anything that
still does require user intervention after they've deployed an Atlas
cluster? Or, is it all automated? This is on the topic of automation,
right?
Rez Kahn (10:37): Yeah. I wish everything was automated, but if it
were, I would not have a job. So, there's obviously a lot of work to do.
The particular area, which is of great interest to me and the company
is, once you deploy an application and the application is scaling, or is
being used by lots of users, and you're making changes to the
application, how do we make sure that the performance of MongoDB itself
is as awesome as possible? Now, that's a very difficult problem to
solve, because you could talk about performance in a lot of different
ways. One of the more obvious proxies of performance is how much time it
takes to get responses to a query back.
Rez Kahn (11:30): You obviously want it to be as low as possible. Now,
the way to get a very low latency on your queries is you can have a very
powerful machine backing that MongoDB instance, but the consequence of
having a very powerful machine backing that MongoDB instance is it can
be very costly. So, how do you manage, how do you make sure costs are
manageable while getting as great of a performance as possible is a very
difficult problem to solve. A lot of people get paid a lot of money to
solve that particular problem. So, we have to characterize that problem
for us, sort of like track the necessary metrics to measure costs,
measure performance.
Rez Kahn (12:13): Then, we need to think about how do I detect when
things are going bad. If things are going bad, what are the strategies I
can put in place to solve those problems? Luckily, with MongoDB, there's
a lot of strategies they can put in place. For example, one of the
attributes of MongoDB is you could have multiple, secondary indexes, and
those indexes can be as complex or as simple as you want, but when do
you put indexes? What indexes do you put? When do you keep indexes
around versus when do you get rid of it? Those are all decisions you
need to make because making indexes is something which is neither cheap,
and keeping them is also not cheap.
Rez Kahn (12:57): So, you have to do an optimization in your head on
when you make indexes, when you get rid of them. Those are the kind of
problems that we believe our expertise and how MongoDB works. The
performance data we are capturing from you using Mongo DB can help us
provide you in a more data-driven recommendations. So, you don't have to
worry about making these calculations in your head yourself.
Michael Lynn (13:22): The costs that you mentioned, there are costs
associated with implementing and maintaining indexes, but there are also
costs if you don't, right? If you're afraid to implement indexes,
because you feel like you may impact your performance negatively by
having too many indexes. So, just having the tool give you visibility
into the effectiveness of your indexes and your index strategy. That's
powerful as well.
Nic Raboy (13:51): So, what kind of visibility would you exactly get?
I want to dig a little deeper into this. So, say I've got my cluster and
I've got tons and tons of data, and quite a few indexes created. Will it
tell me about indexes that maybe I haven't used in a month, for example,
so that way I could remove them? How does it relay that information to
you effectively?
Rez Kahn (14:15): Yeah. What the system would do is it keeps a record
of all indexes that you had made. It will track how much you're using
certain indexes. It will also track whether there are overlaps between
those indexes, which might make one index redundant compared to the
other. Then, we do some heuristics in the background to look at each
index and make an evaluation, like whether it's possible, or whether
it's a good idea to remove that particular index based on how often it
has been used over the past X number of weeks. Whether they are overlaps
with other indexes, and all those things you can do by yourself.
Rez Kahn (14:58): But these are things you need to learn about MongoDB
behavior, which you can, but why do it if it can just tell you that this
is something which is inefficient, and these are the things you need to
make it more efficient.
Michael Lynn (15:13): So, I want to be cognizant that not all of the
listeners of our podcast are going to be super familiar with even
indexes, the concept of indexes. Can you maybe give us a brief
introduction to what indexes are and why they're so important?
Rez Kahn (15:26): Yeah, yeah. That's a really good question. So, when
you're working with a ... So, indexes are not something which is unique
to MongoDB, all other databases also have indexes. The way to look at
indexes, it's a special data structure which stores the data you need in
a manner that makes it very fast to get that data back. So, one good
example is, let's say you have a database with names and phone numbers.
You want to query the database with a name and get that person's phone
number.
Rez Kahn (16:03): Now, if you don't have an index, what the database
software would do is it would go through every record of name and phone
number so that it finds the name you're looking for, and then, it will
give you back the phone number for that particular name. Now, that's a
very expensive process because if you have a database with 50 million
names and phone numbers, that would take a long time. But one of the
things you can do with index is you can create an index of names, which
would organize the data in a manner where it wouldn't have to go through
all the names to find the relevant name that you care about.
Rez Kahn (16:38): It can quickly go to that record and return back the
phone number that you care about. So, instead of going through 50
million rows, you might have to go through a few hundred rows of data in
order to get the information that you want. Suddenly, your queries are
significantly faster than what it would have been if you had not created
an index. Now, the challenge for our users is, like you said, Mike, a
lot of people might not know what an index is, but people generally know
what an index is. The problem is, what is the best possible thing you
could do for MongoDB?
Rez Kahn (17:18): There's some stuff you need to learn. There's some
analysis you need to do such as you need to look at the queries you're
running to figure out like which queries are the most important. Then
for those queries, you need figure out what the best index is. Again,
you can think about those things by yourself if you want to, but there
is some analytical, logical way of giving you, of crunching these
numbers, and just telling you that this is the index which is the best
index for you at this given point in time. These are the reasons why,
and these are the benefit it would give you.
Michael Lynn (17:51): So, okay. Well, indexes sounded like I need
them, because I've got an application and I'm looking up phone numbers
and I do have a lot of phone numbers. So, I'm just going to index
everything in my database. How does that sound?
Rez Kahn (18:05): It might be fine, actually. It depends on how many
indexes you create. The thing which is tricky is because indexes are a
special data structure, it does take up storage space in the database
because you're storing, in my example from before, names in a particular
way. So, you're essentially copying the data that you already have, but
storing it in a particular way. Now, that might be fine, but if you have
a lot of these indexes, you have to create lots of copies of your data.
So, it does use up space, which could actually go to storing new data.
Rez Kahn (18:43): It also has another effect where if you're writing a
lot of data into a database, every time you write a new record, you need
to make sure all those indexes are updated. So, writes can take longer
because you have indexes now. So, you need to strike a happy balance
between how many indexes do I need to get great read performance, but
not have too many indexes so my write performance is hard? That's a
balancing act that you need to do as a user, or you can use our tools
and we can do it for.
Michael Lynn (19:11): There you go, yeah. Obviously, playing a little
devil's advocate there, but it is important to have the right balance-
Rez Kahn (19:17): Absolutely.
Michael Lynn (19:17): ... and base the use of your index on the
read-write profile of your application. So, knowing as much about the
read-write profile, how many reads versus how many writes, how big are
each is incredibly important. So, that's the space that this is in. Is
there a tagline or a product within Atlas that you refer to when you're
talking about this capability?
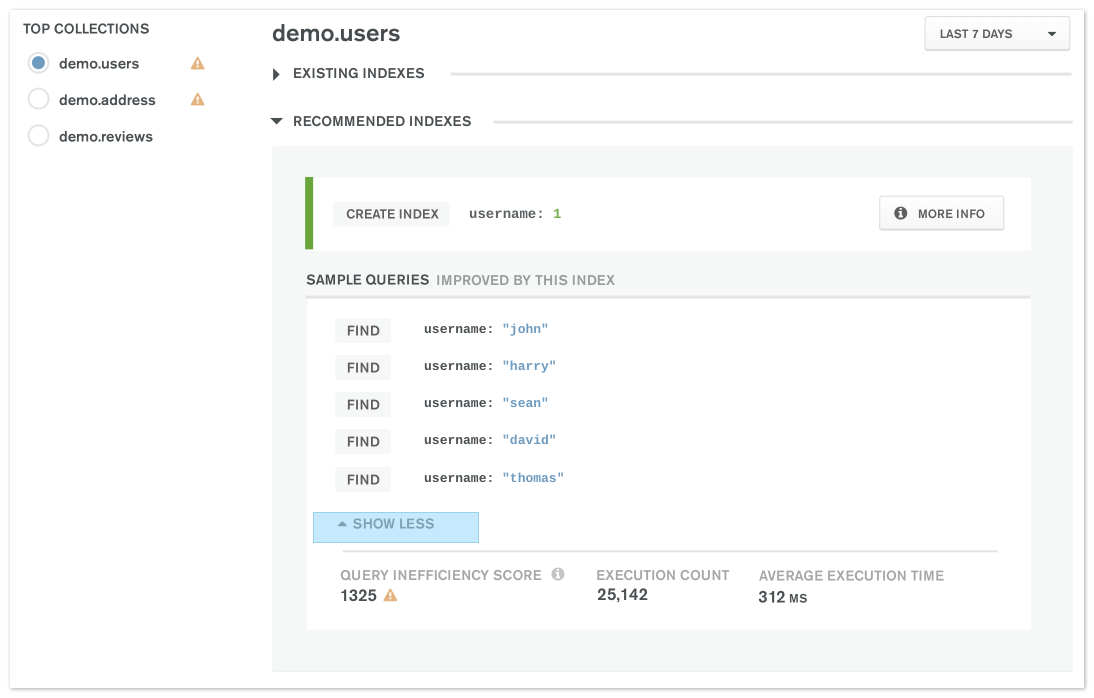
Rez Kahn (19:41): Yeah. So, there's a product called Performance
Advisor, which you can use via the API, or you can use it with the UI.
When you use Performance Advisor, it will scan the queries that ran on
your database and give you a ranked list of indexes that you should be
building based on importance. It will tell you why a particular index is
important. So, we have this very silly name called the impact score. It
would just tell you that this is the percentage impact of having this
index built, and it would rank index recommendations based on that.
Rez Kahn (20:21): One of the really cool things we are building is, so
we've had Performance Advisor for a few years, and it's a fairly popular
product amongst our customers. Our customers who are building an
application on MongoDB Atlas, or if they're changing an application, the
first thing that they do after deploying is they would go to Performance
Advisor and check to see if there are index recommendations. If there
are, then, they would go and build it, and magically the performance of
their queries become better.
So, when you deploy an Atlas cluster, you can say, "I want indexes to be
built automatically." ... as we detect queries, which doesn't have an
index and is important and causing performance degradation, we can
automatically figure out like what the index ought to be.
Rez Kahn (20:51): Because we have had good success with the product,
what we have decided next is, why do even make people go into Atlas and
look at the recommendations, decide which they want to keep, and create
the index manually? Why not just automate that for them? So, when you
deploy an Atlas cluster, you can say, "I want indexes to be built
automatically." If you have it turned on, then we will be proactively
analyzing your queries behind the scenes for you, and as soon as we
detect queries, which doesn't have an index and is important and causing
performance degradation, we can automatically figure out like what the
index ought to be.
Rez Kahn (21:36): Then, build that index for you behind the scenes in
a manner that it's performed. That's a product which we're calling
autopilot mode for indexing, which is coming in the next couple of
months.
Nic Raboy (21:46): So, I have a question around autopilot indexing.
So, you're saying that it's a feature you can enable to allow it to do
it for you on a needed basis. So, around that, will it also remove
indexes for you that are below the percent threshold, or can you
actually even set the threshold on when an index would be created?
Rez Kahn (22:08): So, I'll answer the first question, which is can it
delete indexes for you. Today, it can't. So, we're actually releasing
another product within Performance Advisor called Index Removal
Recommendations, where you can see recommendations of which indexes you
need to remove. The general product philosophy that we have in the
company is, we build recommendations first. If the recommendations are
good, then we can use those recommendations to automate things for our
customers. So, the plan is, over the next six months to provide
recommendations on when indexes ought to be removed.
Rez Kahn (22:43): If we get good user feedback, and if it's actually
useful, then we will incorporate that in autopilot mode for indexing and
have that system also do the indexes for you. Regarding your second
question of, are the thresholds of when indexes are built configurable?
That's a good question, because we did spend a lot of time thinking
about whether we want to give users those thresholds. It's a difficult
question to answer because on one hand, having knobs, and dials, and
buttons is attractive because you can, as a user, can control how the
system behaves.
Rez Kahn (23:20): On the other hand, if you don't know what you're
doing, you could create a lot of problems for yourself, and we want to
be cognizant of that. So, what we have decided to do instead is we're
not providing a lot of knobs and dials in the beginning for our users.
We have selected some defaults on how the system behaves based on
analysis that we have done on thousands of customers, and hoping that
would be enough. But we have a window to add those knobs and dials back
if there are special use cases for our users, but we will do it if it
makes sense, obviously.
Nic Raboy (23:58): The reason why I asked is because you've got the
category of developers who probably are under index, right? Then, to
flip that switch, and now, is there a risk of over-indexing now, in that
sense?
Rez Kahn (24:12): That's a great question. The way we built the
system, we built some fail-safes into it, where the risk of
over-indexing is very limited. So, we do a couple of really cool things.
One of the things we do is, when we detect that there's an index that we
can build, we try to predict things such as how long an index would take
to be built. Then, based on that we can make a decision, whether we'll
automatically build it, or we'll give user the power to say, yay or nay
on building that index. Because we're cognizant of how much time and
resources that index build might take. We also have fail-safes in the
background to prevent runaway index build.
Rez Kahn (24:59): I think we have this configurable threshold of, I
forget the exact number, like 10 or 20 indexes for collections that can
be auto build. After that, it's up to the users to decide to build more
things. The really cool part is, once we have the removal
recommendations out and assuming it works really, if it works well and
users like it, we could use that as a signal to automatically remove
indexes, if you're building too many indexes. Like a very neat, closed
loop system, where we build indexes and observe how it works. If it does
work well, we'll keep it. If it doesn't work well, we'll remove it. You
can be as hands off as you want.
Michael Lynn (25:40): That sounds incredibly exciting. I think I have
a lot of fear around that though, especially because of the speed at
which a system like Atlas, with an application running against it, the
speed to make those types of changes can be onerous, right. To
continually get feedback and then act on that feedback. I'm just
curious, is that one of the challenges that you faced in implementing a
system like this?
Rez Kahn (26:12): Yeah. One of the big challenges is, we talked about
this a lot during the R&D phase is, we think there are two strategies
for index creation. There is what we call reactive, and then there is
proactive. Reactive generally is you make a change in your application
and you add a query which has no index, and it's a very expensive query.
You want to make the index as soon as possible in order to protect the
MongoDB instance from a performance problem. The question is, what is
soon? How do you know that this particular query would be used for a
long time versus just used once?
Rez Kahn (26:55): It could be a query made by an analyst and it's
expensive, but it's only going to be used once. So, it doesn't make
sense to build an index for it. That's a very difficult problem to
solve. So, in the beginning, our approach has been, let's be
conservative. Let's wait six hours and observe like what a query does
for six hours. That gives us an adequate amount of confidence that this
is a query which is actually going to be there for a while and hence an
index makes sense. Does that make sense, Mike?
Michael Lynn (27:28): Yeah, it does. Yeah. Perfect sense. I'm thinking
about the increased flexibility associated with leveraging MongoDB in
Atlas. Now, obviously, MongoDB is an open database. You can download it,
install it on your laptop and you can use it on servers in your data
center. Will any of these automation features appear in the non-Atlas
product set?
Rez Kahn (27:58): That's a really good question. We obviously want to
make it available to as many of our customers as possible, because it is
very valuable to have systems like this. There are some practical
realities that make it difficult. One of the reality is, when you're
using Atlas, the underlying machines, which is backing your database, is
something that we can quickly configure and add very easily because
MongoDB is the one which is managing those machines for you, because
it's a service that we provide. The infrastructure is hidden from you,
which means that automation features, where we need to change the
underlying machines very quickly, is only possible in Atlas because we
control those machines.
Rez Kahn (28:49): So, a good example of that is, and we should talk
about this at some point, we have auto scaling, where we can
automatically scale a machine up or down in order to manage your load.
Even if you want to, we can actually give that feature to our customers
using MongoDB on premise because we don't have access to the machine,
but in Atlas we do. For automatic indexing, it's a little bit easier
because it's more of a software configuration. So, it's easier for us to
give it to other places where MongoDB is used.
Rez Kahn (29:21): We definitely want to do that. We're just starting
with Atlas because it's faster and easier to do, and we have a lot of
customers there. So, it's a lot of customers to test and give us
feedback about the product.
Michael Lynn (29:31): That's a great answer. It helps me to draw it
out in my head in terms of an architecture. So, it sounds like there's a
layer above ... MongoDB is a server process. You connect to it to
interface with and to manage your data. But in Atlas, there's an
additional layer that is on top of the database, and through that layer,
we have access to all of the statistics associated with how you're
accessing your database. So, that layer does not exist in the
downloadable MongoDB today, anyway.
Rez Kahn (30:06): It doesn't. Yeah, it doesn't.
Michael Lynn (30:08): Yeah.
Rez Kahn (30:09): Exactly.
Michael Lynn (30:09): Wow, so that's quite a bit in the indexing
space, but that's just one piece of the puzzle, right? Folks that are
leveraging the database are struggling across a whole bunch of areas.
So, what else can we talk about in this space where you're solving these
problems?
Rez Kahn (30:26): Yeah. There is so much, like you mentioned, indexing
is just one strategy for performance optimization, but there's so many
others, one of the very common or uncommon, whoever you might ask this,
is what should the schema of your data be and how do you optimize the
schema for optimal performance? That's a very interesting problem space.
We have done a lot of ticking on that and we have a couple of products
to help you do that as well.
Rez Kahn (30:54): Another problem is, how do we project out, how do we
forecast what your future workload would be in order to make sure that
we are provisioning the right amount of machine power behind your
database, so that you get the best performance, but don't pay extra
because you're over over-provisioned? When is the best time to have a
shard versus scale up vertically, and what is the best shard key to use?
That is also another interesting problem space for us to tackle. So,
there's a lot to talk about [crosstalk 00:31:33] we should, at some
point.
Michael Lynn (31:36): These are all facets of the product that you
manage?
Rez Kahn (31:39): These are all facets of the product that I manage,
yeah. One thing which I would love to invite our users listen to the
podcast, like I mentioned before, we're building this tool called
Autopilot Mode for Indexing to automatically create indexes for you.
It's in heavy engineering development right now, and we're hoping to
release it in the next couple of months. We're going to be doing a private preview program for that particular product, trying to get around
hundred users to use that product and get early access to it. I would
encourage you guys to think about that and give that a shot.
Michael Lynn (32:21): Who can participate, who are you looking to get
their hands on this?
Rez Kahn (32:26): In theory, it should be anyone, anyone who is
spending a lot of time building indexes would be perfect candidates for
it. All of our MongoDB users spend a lot of time building indexes. So,
we are open to any type of companies, or use cases, and we're very
excited to work with you to see how we can make the product successful
for it, and use your feedback to build the next version of the product.
Michael Lynn (32:51): Great. Well, this has been a phenomenal
introduction to database automation, Rez. I want to thank you for taking
the time to talk with us. Nick, before we close out, any other questions
or things you think we should cover?
Nic Raboy (33:02): No, not for this episode. If anyone has any
questions after listening to this episode, please jump into our
community. So, this is a community forum board, Rez, Mike, myself, we're
all active in it. It's community.mongodb.com. It's a great way to get
your questions answered about automation.
Michael Lynn (33:21): Absolutely. Rez, you're in there as well. You've
taken a look at some of the questions that come across from users.
Rez Kahn (33:27): Yeah, I do that occasionally. Not as much as I
should, but I do that.
Michael Lynn (33:32): Awesome.
Nic Raboy (33:32): Well, there's a question that pops up, we'll pull
you.
Michael Lynn (33:34): Yeah, if we get some more questions in there,
we'll get you in there.
Rez Kahn (33:37): Sounds good.
Michael Lynn (33:38): Awesome. Well, terrific, Rez. Thanks once again
for taking the time to talk with us. I'm going to hold you to that.
We're going to take this in a series approach. We're going to break all
of these facets of database automation down, and we're going to cover
them one by one. Today's been an introduction and a little bit about
autopilot mode for indexing. Next one, what do you think? What do you
think you want to cover next?
Rez Kahn (34:01): Oh, let's do scaling.
Nic Raboy (34:02): I love it.
Michael Lynn (34:03): Scaling and auto scalability. I love it.
Awesome. All right, folks, thanks.
Rez Kahn (34:08): Thank you.
An important part of ensuring efficient application performance is
modeling the data in your documents, but once you've designed the
structure of your documents, it's absolutely critical that you continue
to review the read/write profile of your application to ensure that
you've properly indexed the data elements most frequently read. MongoDB
Atlas' automated index management can help as the profile of your
application changes over time.
Be sure you check out the links below for suggested reading around
performance considerations. If you have questions, visit us in the
Community Forums.
In our next episodes in this series, we'll build on the concept of
automating database management to discuss automating the scaling of your
database to ensure that your application has the right mix of resources
based on its requirements.
Stay tuned for Part 2. Remember to subscribe to the
Podcast to make sure that you don't miss
a single episode.
Check out the following resources for more information: