Business intelligence tools are software that can collect and process huge amounts of business data from various semi-structured and unstructured data sources, like images, text files, videos, books, and public health records; integrate the data; prepare the data for analytics; and provide actionable insights to facilitate data-driven decisions.
Table of contents
- What is business intelligence (BI)?
- What is a business intelligence tool?
- Why use business intelligence tools?
- Types of business intelligence software
- Key business intelligence software features
- Who uses business intelligence software?
- Relevant BI software trends
- Choosing the best business intelligence software solutions
- Business intelligence tools and MongoDB
- Next steps
- FAQs
What is business intelligence (BI)?
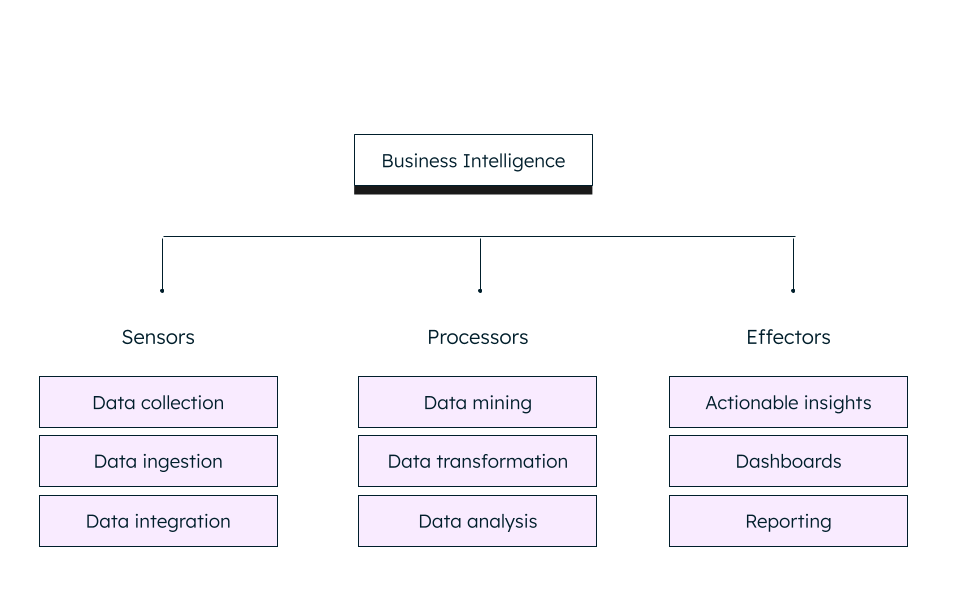
Organizations today are striving to become intelligent, just like humans. Continuing the analogy, we can divide an intelligent organization into three groups:
Sensors are like the senses that collect data from various data sources and integrate them.
Processors are like the brain that processes the data (data analysis) and turns it into knowledge or insights.
Effectors are like our hands and legs that perform the action based on the signal given by processors (brain). Effectors consist of a flexible team of technical and non-technical people and resources.
Business intelligence is an umbrella term comprising these three processes along with the right technologies to create intelligent, data-driven organizations.
 Here are common examples of business intelligence:
Here are common examples of business intelligence:
Retail companies perform target marketing by managing the preferences of millions of users through business intelligence.
Company HR uses BI tools to scan thousands of profiles and map job requirements.
Logistic companies use business intelligence to optimize routes and find out the fastest routes for shipments.
An e-commerce platform utilizes business intelligence to analyze website traffic, sales data, and customer behavior to enhance user experience and increase conversion rate.
What is a business intelligence tool?
A business intelligence tool is a software that can collect, process, and analyze data, generating reports and dashboards to reveal valuable insights. These tools can perform online analytical processing (OLAP), predictive and augmented analytics, visual analytics, and embedded analytics.
Earlier BI tools were limited to querying and generating reports, which did not help much with making timely decisions. Modern BI tools like Tableau and Microsoft PowerBI are more flexible and adaptive, offer visual data discovery, help generate actionable insights, prepare reports and dashboards, and build visualizations and performance scorecards to display KPIs and business metrics.
Why use business intelligence tools?
BI reporting tools can help businesses collect and integrate data from multiple sources, and present it in an easy-to-understand manner for further analysis, reporting, and actions. BI tools create quality data from the raw data and work on the past and present data to analyze market trends.
Although BI tools with advanced analytical capabilities are paid, many open-source BI tools provide good BI reporting and analytics.
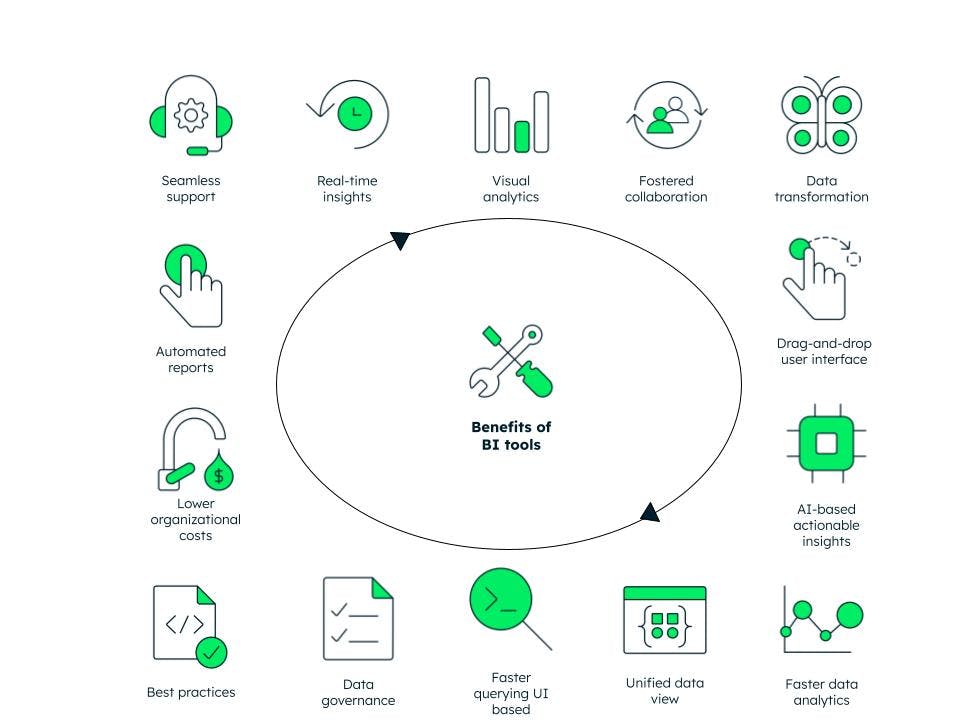
There are many advantages of business intelligence tools:
Combining data from external and internal resources for a unified view via dashboards
Increased organizational efficiency by reducing dependency on manual reporting and data preparation tasks, thereby ensuring faster analysis and quicker decisions
Improved customer experience by understanding user preferences and behavior patterns based on past and current data
Governed data to ensure both data security and data quality—most advanced BI tools provide in-built data governance like data auditing, security, and authorization
Increased competitive advantage by proactive actionable insights based on forecasts given by BI tools
Increased revenue and profits by analyzing past, present, and future trends to understand customers, offer targeted marketing, and improve products and services
Drag-and-drop-based interface for querying making it easier even for non-technical staff to query and visualize data
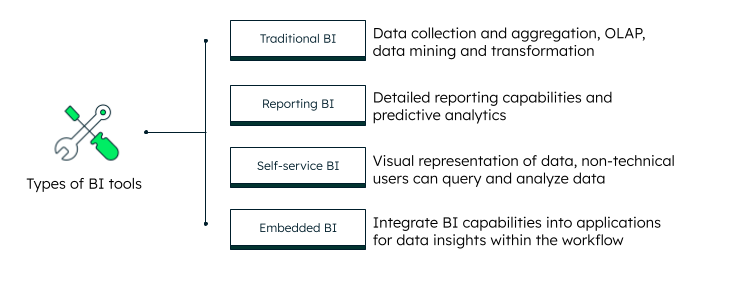
Types of business intelligence software
To choose the right business intelligence tool for your business, it helps to make a BI tools comparison based on the tool type and features. The different types of business intelligence tools are:
Traditional BI
Traditional BI software supports OLAP, ad-hoc analytics, and data visualization and is suitable for processing large datasets. While some aspects can be user-friendly, these tools often require more technical expertise compared to modern self-service BI solutions. Examples include SAP Crystal Reports and IBM Cognos.
Reporting BI
Reporting BI can perform all the regular tasks like preparing reports and dashboards in a fixed-format design. You can think of them like an Excel spreadsheet. Reporting BI tools make complex reports easy and can handle datasets with a few thousand documents. Examples are FineReport and the Google data studio.
Self-service BI
Self-service BI is the most common type, as most traditional BI software is not able to fulfill the complete data analytics needs of organizations. For example, Chipotle had to replace its traditional BI for a self-service BI in order to create a single view of operations that would track effectiveness at a national level.
Self-service BI provides all the features of reporting and traditional BI along with data cleaning and exploration tools, and advanced AI-driven analytics. These tools can be used by both technical and non-technical users. Self-service BI is also called agile BI. Some examples are Tableau Desktop, Microsoft Excel, and Microsoft Power BI.
Embedded BI
Embedded BI allows integration of self-service BI into your business applications. These tools support better visualizations, interactive reporting, dashboards, and real-time analytics. Embedded BI can also become a part of workflow automation in advanced scenarios. SAP and MongoDB Charts are some top embedded business intelligence software.
Key business intelligence software features
The best business intelligence tools have a few or more of the following features:
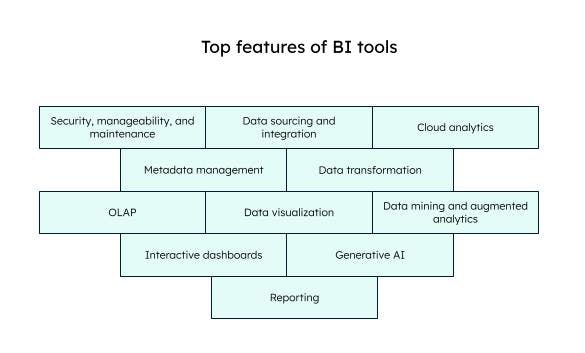
Security, manageability, and maintenance: BI tools provide good platform security and disaster recovery. Users can monitor usage and manage access, authorization, and authentication.
Data sourcing and integration: BI software can connect to real-time and static data from both internal and external systems—for example, spreadsheets, social media, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, data warehouses, and data lakes—integrate all the data, and analyze it together.
Cloud analytics: Many BI tools like Sisense, MongoDB Charts, and Google’s data studio are multi-cloud capable, meaning they can build, deploy, and manage analytics on multiple cloud environments. Users can visualize and explore data on the cloud platform.
Metadata management: BI software can manage metadata centrally, including extracting, storing, processing, sharing, and publishing metadata. Metadata refers to measures, indicators, hierarchies, key performance indicators, sales data, and other data that can help in business analytics.
Data transformation: BI tools automatically perform the ETL (extract, transform, load) process and prepare data for analytics. Integrity checks are done to check data accuracy and consistency. Data is transformed to a common format and then loaded into a data warehouse or data lake. Some tools, like SAS, provide AI-driven data preparation suggestions, voice integration, and smart narratives.
OLAP: OLAP is a means to sort, aggregate, filter, slice, dice, and group data to present it to users. Users can extract and view data from multiple sources. OLAP gives a multidimensional view of data and is good for analysis of past data.
Data visualization: Visualizations make it easy to find trends and insights in data through graphs, multi-layered charts, geospatial maps, custom maps, and many more. Most BI tools support advanced graphs and interactive displays, and automatically suggest the best graphical representation for a particular query.
Data mining and augmented analytics: BI tools can mine raw data to find information and wisdom in the form of patterns and trends. This includes advanced analytics and techniques like statistics and machine learning algorithms.
Dashboards: A dashboard is like a customized home page based on the role of the BI tool user. It summarizes all the reports, key business metrics, and important graphics to create data visualizations in a single view.
Generative AI: BI tools leverage generative AI for predictive analytics, automated insights, natural language queries, and custom visualizations.
Reporting: BI tools improve and automate ad hoc reporting capabilities by customizing the metrics. This means each user can look at the reports they want to, rather than generating hundreds of bulky reports. The reports can be easily shared and collaborated across the team.
MongoDB Charts as a business intelligence tool provides all the key features like reporting, predictive analytics, dashboards, data visualization, and OLAP, all embedded into MongoDB’s cloud data service, MongoDB Atlas.
Who uses business intelligence software?
As the capabilities of business intelligence platforms are increasing, so are the users. Earlier, the major users of BI software were the business analysts and the IT team. Now, business intelligence reporting and analytics tools are used by many teams within a company. Some typical users of BI software include data analysts and data scientists who use them to find insights, visualize patterns and trends, generate and share reports with stakeholders, and help with the decision-making process. Similarly, business analysts look at dashboards, reports, and visualizations to get insights, play around with data, and discuss possible solutions to problems with stakeholders and key business partners. Even CEOs use business intelligence software and reporting tools to look for organizational trends, innovation in processes, overall company growth, and operational efficiencies, and to make better business decisions.
Relevant BI software trends
BI tools are becoming increasingly important because of more digitalization post COVID-19. From schools to offices, everyone seems to have an online presence now. This has led to new trends within business intelligence tools:
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) and automation: Many of the best business intelligence tools already include AI and machine learning for automating workflows and generating insights. With value adds like smart narratives and voice integration, there is a lot of focus on enhancing overall user experience.
Data governance: With more data shared, data governance—meaning data quality and data security—is becoming critical.
Cloud adoption: Cloud BI is more beneficial for cost efficiency and flexibility, especially because of the increase in remote working environments.
Data literacy: Data literacy is the ability to read, comprehend, analyze, and communicate effectively with data. Data literacy can bridge the gap between analysts and business users, and make BI reporting and visualizations easy to interpret.
Self-service BI: Self-service BI is already trending because users with very little technical skills can also utilize data effectively. Business users can create BI reports without depending on technical staff, thereby reducing the time required to get insights.
Choosing the best business intelligence software solutions
The right business intelligence software should be able to solve the main purpose, i.e., query the right data and get useful insights to drive business solutions. Here are some questions you should answer before choosing a BI tool:
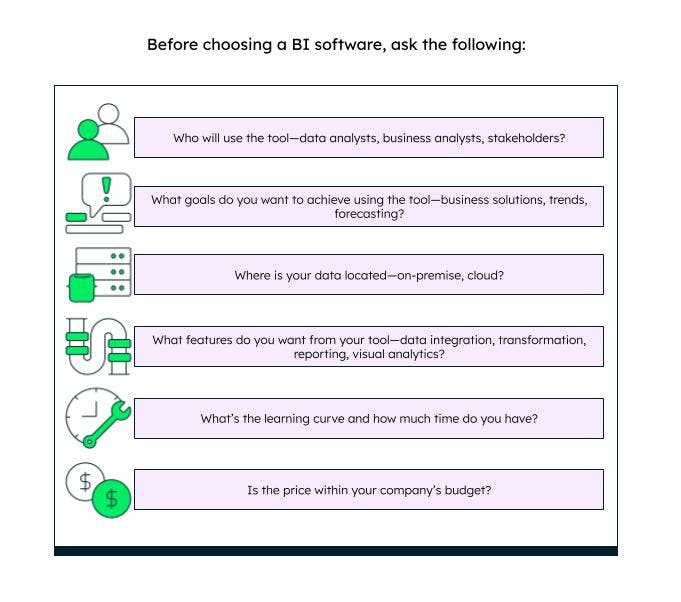
Who will use the tool?
While data analysts are technically sound, business users are mostly non-technical and they should be able to analyze data without the need to manually write queries. Tools like Qlik, Tableau, and Microsoft Power BI have an intuitive interface and provide self-service capabilities for business users. MongoDB Charts provides advanced visualization capabilities within the Atlas ecosystem.
What is the goal you want to achieve?
Opt for a tool that solves your business problem over one that has a lot of features that won’t be useful for your business objectives. For example, you can choose a tool that already has prepackaged solutions for the specific objective your business wants to achieve.
Where is your data located?
If your data is spread across cloud platforms and on-premise data centers, choose a BI reporting tool that can seamlessly integrate all the historic and real-time data. For example, MongoDB Atlas helps source data from multiple platforms and store it in any format for better transformation.
Do you want your BI tool to transform data?
More often than not, you will need a BI tool that collects data from various sources, cleans the data, and transforms it to make it useful for analysis. The MongoDB aggregation framework provides advanced queries to filter and transform data as per your business needs.
What is the learning curve?
To start, choose a user-friendly BI tool that is intuitive and easy to learn so you can quickly get onboard with it. For example, tools like Power BI and MongoDB Compass have lower learning curves compared to tools with extensive functionalities like SAS or Qlik.
Is the price within your company’s budget?
BI software vendors typically provide two pricing models: on-premise and cloud hosting. Consider the model that you prefer and conduct a price comparison.
Gartner's magic quadrant for analytics and BI platforms shows Microsoft, Tableau, and Qlik as leaders.
The MongoDB Connector for Business Intelligence provides an easy interface to work with the aforementioned BI tools.
Business intelligence tools and MongoDB
BI tools enable organizations to make better business decisions by automating data analytics and providing valuable insights.
The MongoDB Atlas Live Migration Service allows for seamless migration of data from existing environments to MongoDB Atlas with minimal impact on applications, making it easier to connect and analyze data using BI tools.
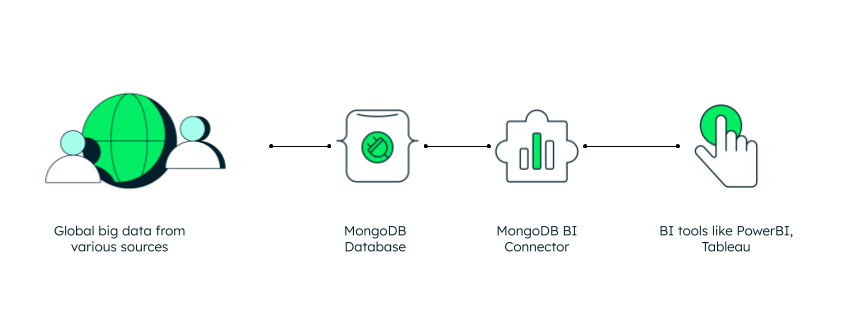 MongoDB's Atlas SQL Interface, connectors, and drivers facilitate seamless connections to various BI software, allowing users to query and visualize data natively with SQL-based tools while maintaining the document model's flexibility. Custom-built connectors for Microsoft Power BI and Tableau, along with updated Atlas JDBC and ODBC Drivers, eliminate the need for complex ETL processes. These tools leverage SQL-92 compatible mongosqld and Atlas Data Federation to enable querying across Atlas clusters and cloud storage. This integration provides a first-class querying experience, making it easier to find insights from live application data using familiar SQL knowledge and BI tools.
MongoDB's Atlas SQL Interface, connectors, and drivers facilitate seamless connections to various BI software, allowing users to query and visualize data natively with SQL-based tools while maintaining the document model's flexibility. Custom-built connectors for Microsoft Power BI and Tableau, along with updated Atlas JDBC and ODBC Drivers, eliminate the need for complex ETL processes. These tools leverage SQL-92 compatible mongosqld and Atlas Data Federation to enable querying across Atlas clusters and cloud storage. This integration provides a first-class querying experience, making it easier to find insights from live application data using familiar SQL knowledge and BI tools.
Tableau Connector
The Tableau Connector for MongoDB Atlas enables querying live Atlas data with access to native Tableau features, such as custom SQL, calculated columns and raw SQL pass through, and split columns. Learn more.
Power BI Connector
Certified by Microsoft, the PowerBI Connector for MongoDB Atlas enables querying live Atlas data and access to native Microsoft Power BI features, including full Power Query, Power BI Desktop, and Service functionality. Learn more.
JDBC driver
Leverage the Atlas SQL JDBC driver to connect your SQL-based tools that accept an Open Database Connectivity API. Learn more.
ODBC driver
Leverage the Atlas SQL ODBC driver to connect your SQL-based tools that accept an Open Database Connectivity API. Learn more.
Next steps
Now that you have firsthand information on BI tools, you can enable the BI Connector for Atlas and start using MongoDB with your choice of BI tools. If your data is in MongoDB Atlas, consider using MongoDB Charts, the SaaS BI tool that provides rich dashboards, real-time analytics, and data visualizations.
FAQs
What are the tools used in business intelligence?
What are the best business intelligence tools?
Almost all the modern BI tools provide features like visualization, dashboards, easy reporting, analytics, and cloud support. The choice of best business intelligence tools depends on your business needs and goals.
What are business intelligence tools and techniques?
What is the business intelligence process?
Business intelligence processes consist of the following steps:
- Defining business goals
- Gathering the required data
- Data preparation and transformation
- Data processing and analysis
- Data visualization
- Feedback and decision-making
What are BI tools and their uses?
BI tools help businesses analyze huge amounts of data automatically to improve their processes and increase revenue. These tools can be used by technical and non-technical users alike because of their features like dashboards, automated reporting, data visualization, and drag-and-drop functionality. Some important uses of these tools are:
Creating dashboards to view analytics results.
Generating reports to make strategic decisions with stakeholders.
Querying data for advanced analytics.
Applying intelligent AI and ML capabilities to get accurate insights.
Integrating business intelligence into applications for seamless workflow.
Using cloud-based analytics for better reach and collaboration.